What is magnet thermal aging?
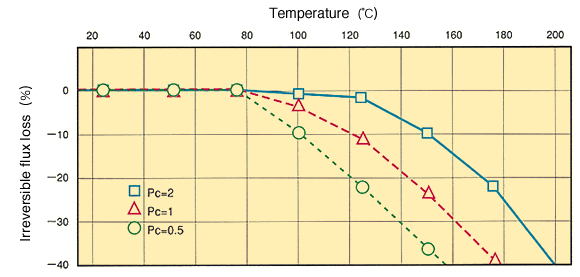
Even though we usually say “permanent magnet”, but magnets do not remain magnetism permanently. In general, permanent magnets are gradually demagnetized by the impact of heat variations. This behavior of magnet can be determined by total flux change over time for a given temperature, also known as “flux loss”.
What kinds of total flux loss can be divided into?
The total flux loss can be divided into reversible loss, recoverable irreversible loss and unrecoverable irreversible loss (structural loss).
What are characteristics of reversible loss?
The reversible loss can be recovered when the temperature returns to its initial temperature from operating temperature. This kind of flux loss can’t be removed by aging treatment (heat stabilization), and this part of loss are very small.
What are characteristics of recoverable irreversible loss?
This part of flux loss usually lost after temperature recovery. These losses are only recoverable by re-magnetization.
What are characteristics of unrecoverable irreversible loss?
This kind of loss is also called structural loss. The structural loss can’t recoverable even if re-magnetization.
Why consider the total flux loss during engineering design?
In some application of magnet, the magnets are usually exposed at an elevated temperature which causes flux reduction. Designer need to fully consider the factors of flux loss can improve the service life of magnets.
How to implement aging treatment of magnets?
The magnet should be stabilized by exposing is to elevated temperature for specify time, and the magnets will more stable during its use.
Which factors have impact on magnet thermal aging?
- Shape of magnet.
- Operating condition and time.
- Magnetic properties of magnet.
- Composition of magnet.
- Microstructure of magnet.
- Surface state of magnet.
- Coating property of magnet,
