Neodymium magnets are consists of an alloy of Neodymium, Boron, and Iron. Neodymium disc magnets have become a preferred solution for a wide variety of industrial and civil applications. Neodymium disc magnet is typically measured by the diameter and thickness, then its thickness is always smaller than the diameter. The great majority of Neodymium disc magnet are axially magnetized and widely served various types of application, such as holding purpose and speaker magnet. Diametrically magnetized pattern is also available for circular magnet and most of diametrically magnetized Neodymium disc magnet are used as the sensor magnet. Production efficiency of Neodymium disc magnet has gained a remarkable development with the widely application of multi-wire sawing.

How to Increase Pull Force of Neodymium Disc Magnet?
Consumers from holding or mounting application commonly have the lively interest in pull force of Neodymium disc magnets. Pull force of regular axial magnetized Neodymium disc magnet can be enhanced through increasing thickness and diameter, select higher grade (e.g. N52 instead N35), shorten air gap from attracting workpiece, or utilize any combination of the above solutions. In addition, pull force of axially multipole magnetized magnet is definitely higher than pure axially magnetized magnet for the same Neodymium disc magnet.
Neodymium Disc Magnet Calculator
Notes:
- This calculator adapts to non-coating and non-chamfer magnet.
- Gauss value is based on Biot-Savart law and applicable to calculate gauss value of pole face’s geometric center.
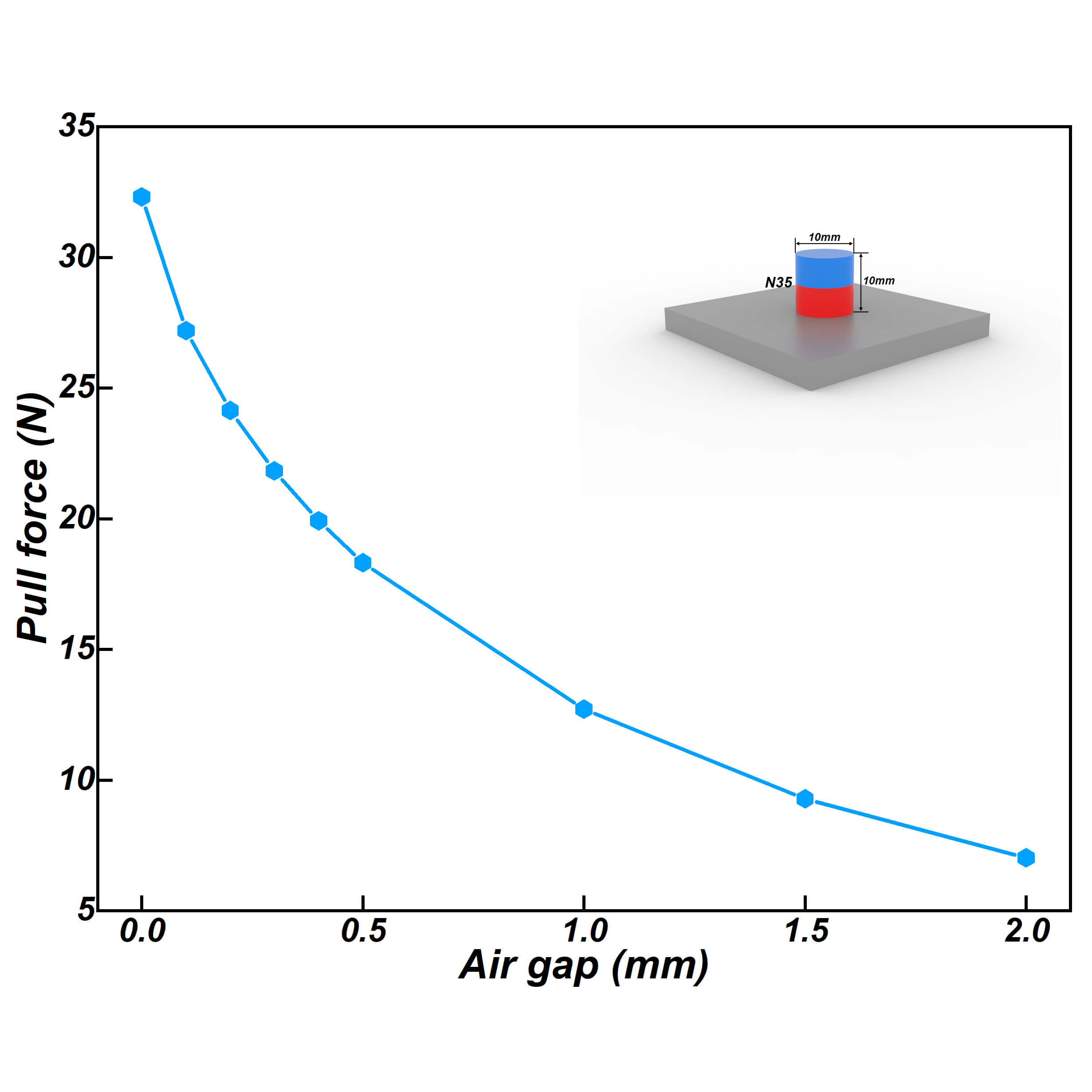
- Surface gauss value decreased as the air gap increased, therefore, both encapsulation of hall component and neglected air gap have the significant role on the accuracy of gauss value. We recommend users set the air gap between 0.3 and 0.5mm.
- Measurement repeatability of surface gauss is relatively low even testing point is the geometric center. It must be pointed that surface gauss cannot represent the overall magnetic performance of the magnet in comparison with magnetic flux or magnetic moment.
- Air gap between magnet and steel plate in calculator is 0mm. In reality, even very small air gap will generate dramatic influence on the pull force in both theoretical calculations and the actual measurement.
- Besides magnet’s material, grade, and dimension, pull force is also impacted by steel plate’s material, composition, and surface condition. Steel plate should be thick enough to carry all magnetic flux or result in the low pull force owing to magnetic saturation.
- Above calculation results are only for reference.