The majority of permanent magnets are magnetized prior before serving for their intended applications. Magnetization process refers to applying a magnetic field along the orientation direction of the permanent magnet and achieved technical saturation with the increased external magnetic field strength. Each type of permanent magnetic material needs distinct magnetic field strength to fulfill technical saturation in magnetization direction. Remanence Br and intrinsic coercivity Hcj will be less than its due values unless external magnetic field strength lower the technical saturation magnetic field.
How to Magnetize Permanent Magnet?
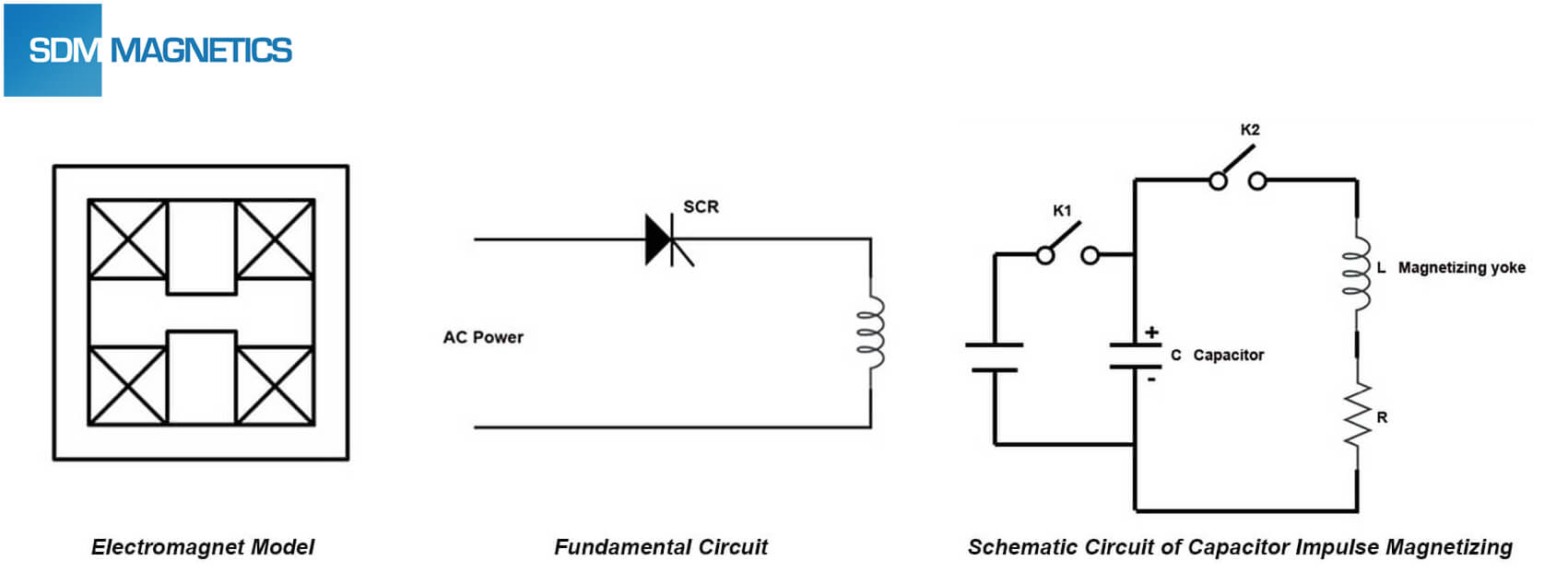
Permanent magnet can be magnetized via either direct current magnetization or impulse magnetization. Direct current system includes direct current power and electromagnet or magnetizing fixture. Direct current magnetic field will be generated after direct current entered the coil. Magnetic field strength between two poles of the electromagnet is proportional to the coil turns N and current intensity I, and inversely proportional to the gap between two poles. Both electromagnet and magnetizing fixture are extremely difficult to magnetize high-coercivity permanent magnet to technical saturation status. For impulse magnetization, the capacitor will be charged after rectification, then the electrical energy in capacitor instantaneous discharge to the magnetizing fixture. Magnetizing fixture can generate the pulsed magnetic field during the instantaneous strong current through it. Therefore, permanent magnet in coil will be magnetized.
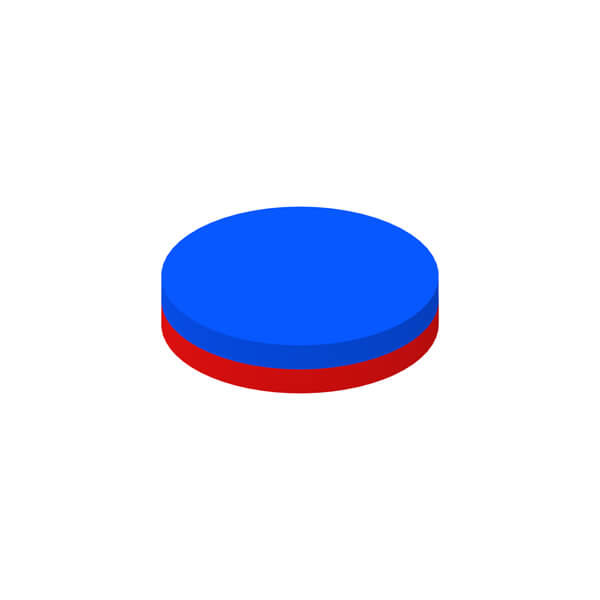
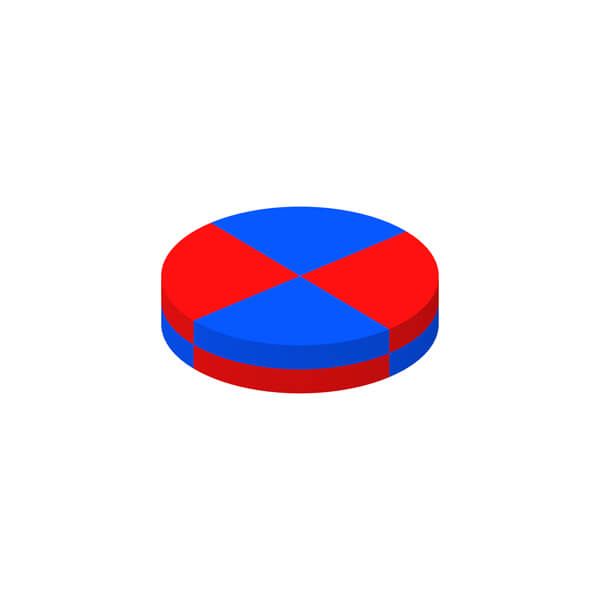
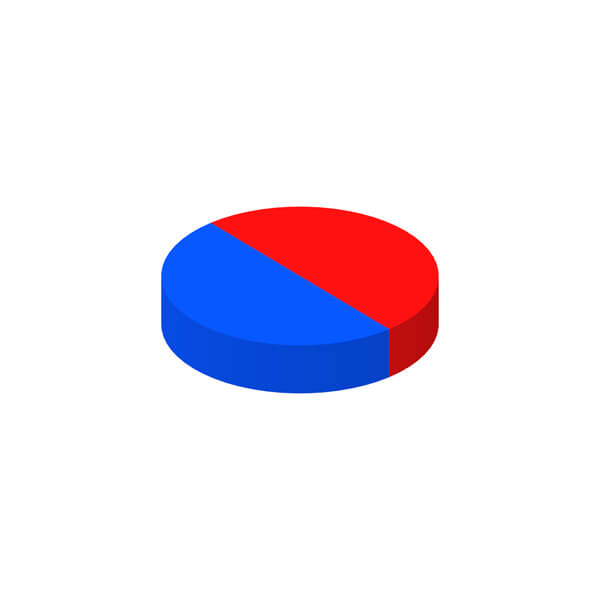
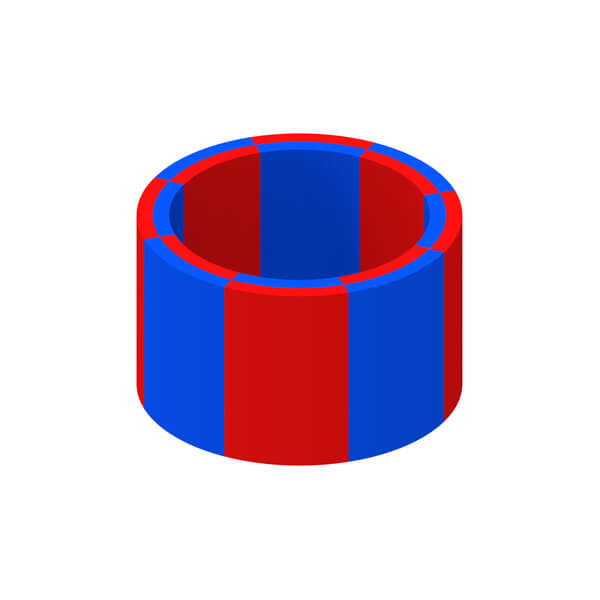
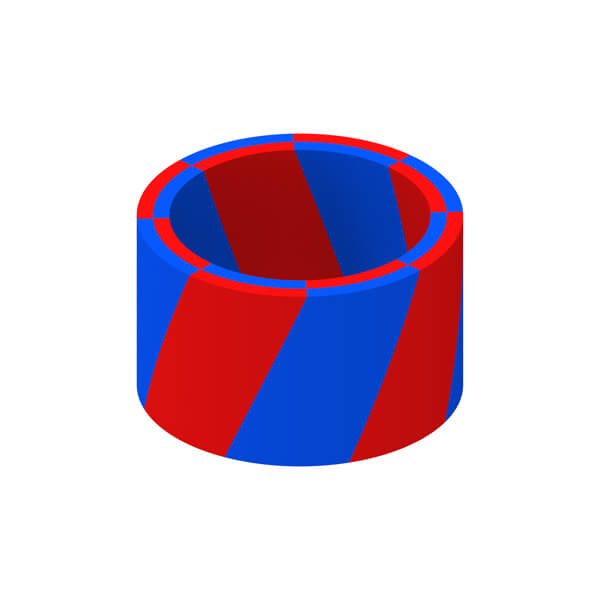
Magnetization Diretion of Permanent Magnet
Permanent magnet can be divided into isotropic type and anisotropic type according to whether has a preferred direction of magnetization or not. For anisotropic magnet, various magnetization patterns can be also achieved so long as not conflicting with its orientation direction.